Atrial Fibrillation
Normally, the electrical signals that cause the heart to beat flow through the heart in an orderly and regular way. This is known as sinus rhythm.
Unfortunately, the electrical signals may flow in an abnormal manner and this is known as arrhythmia. The most common arrhythmia is known as atrial fibrillation (AF) and this becomes more common as people get older. It is estimated that at least 7% of people over the age of 65 have AF.
AF is important because it is a common cause of stroke and on average, people with AF are 5 times more likely to have a stroke. Fortunately, there are effective treatments which can reduce this risk.
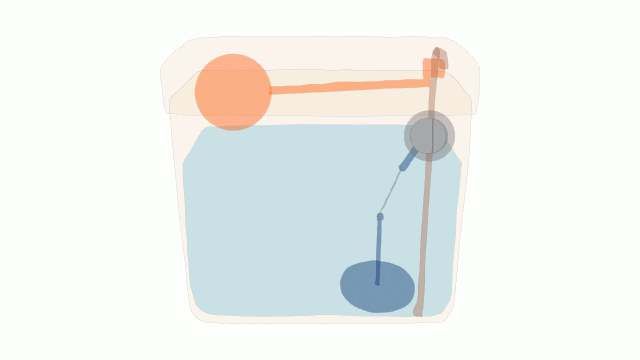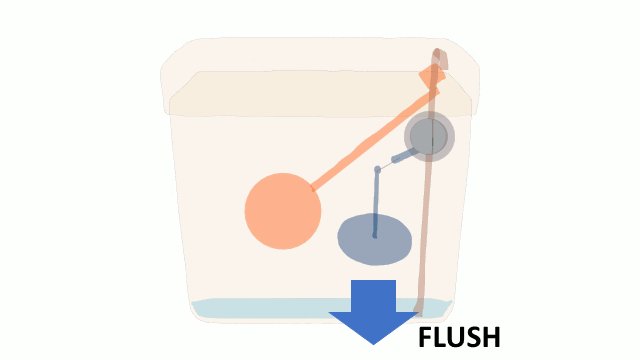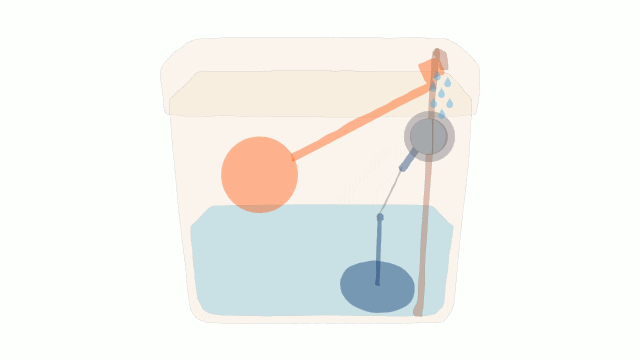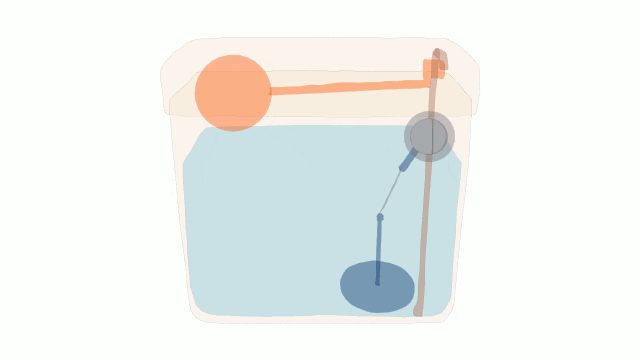
A Water Cistern
Modern water cisterns have small and large buttons to adjust the volume of the flush.
The cistern refills after each flush. This can take some time and may result in frustation if 2 flushes are required in quick succession.
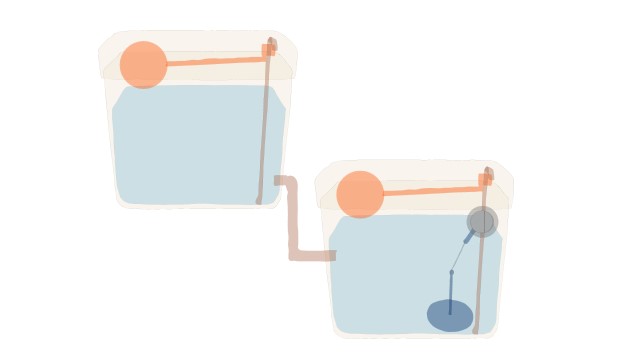
A Super Water Cistern
One possible solution is to have another cistern connected to and above the first cistern. This would allow more rapid filling after each flush and so avoid frustration.
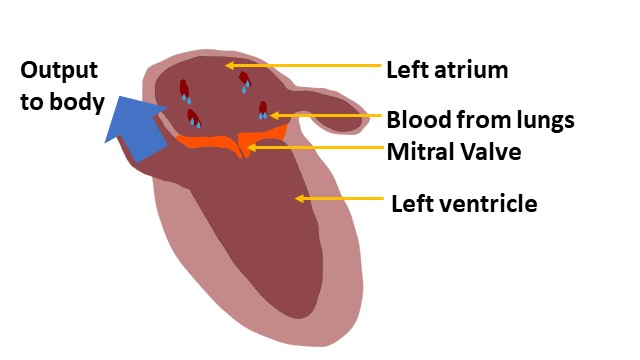
The Atria of the Heart
The main pumps of the heart are known as the ventricles. The right ventricle (RV) pumps blood to the lungs and the left ventricle (LV) pumps blood to the rest of the body.
The left and right atrium are connected to and above the ventricles. Both atria fill continuously. The left atrium fills with blood from the lungs and after each LV beat, the mitral valve opens and the LV fills quickly. Most of this filling is passive but towards the end, the left atrium also contracts and this contributes to 30% of LV filling.
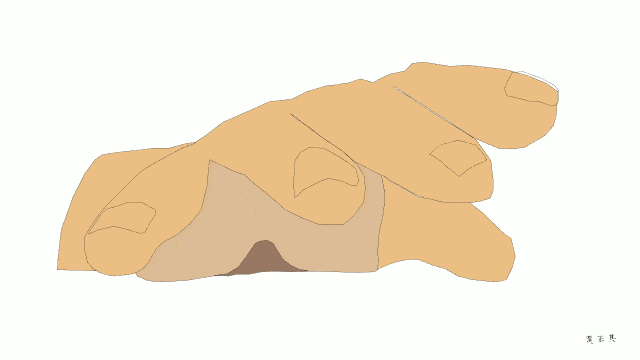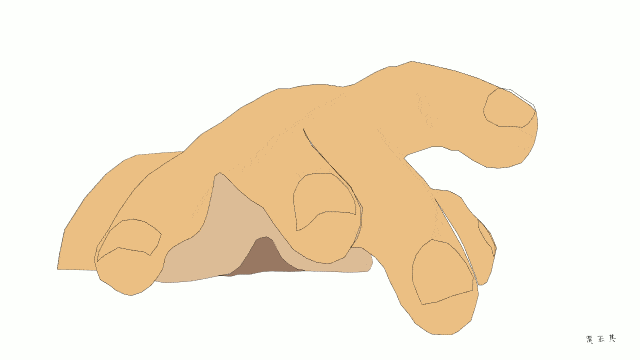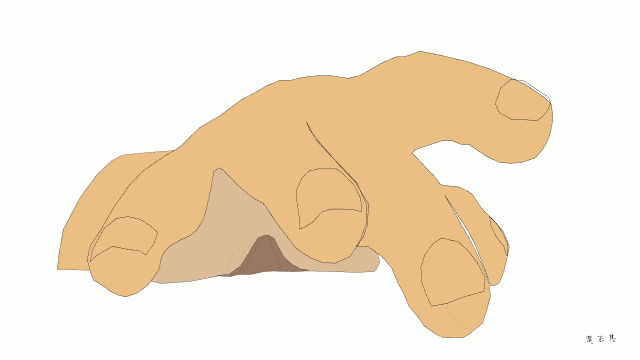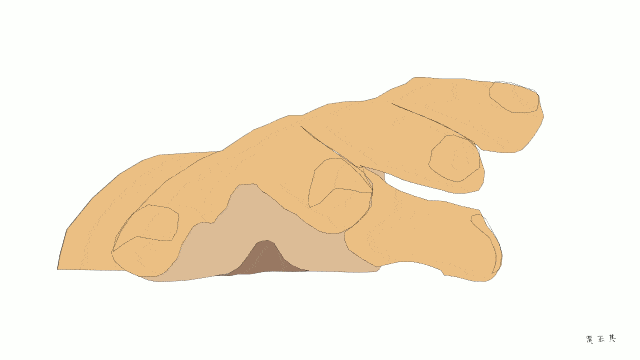
Atrial fibrillation
The arrangement of the atria and ventricles provide for fast efficient filling of the ventricles between each heart beat. In sinus rhythm, the alternate contraction of the atria and ventricles are well co-ordinated.
In atrial fibrillation, electricity flows randomly through the atria. The atria do not contract. They tremor at a high rate. The ventricles do contract but in a completely irregular (“irregularly irregular”) manner. In addition, the ventricles are usually beating too quickly.
Symptoms of AF
Patients with AF may experience palpitations which is an awareness of the heart beat. Doctors may ask patients to “tap out” their palpitations and AF is suspected if the rhythm is completely irregular.

Smooth (Laminar) Flow
In sinus rhythm, blood flow through the atria is smooth and this is known as laminar flow.

Turbulent Flow
In atrial fibrillation, the atria are tremoring and the blood flow is swirling and turbulent.
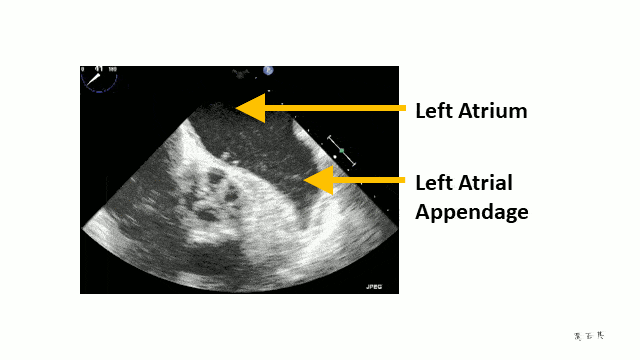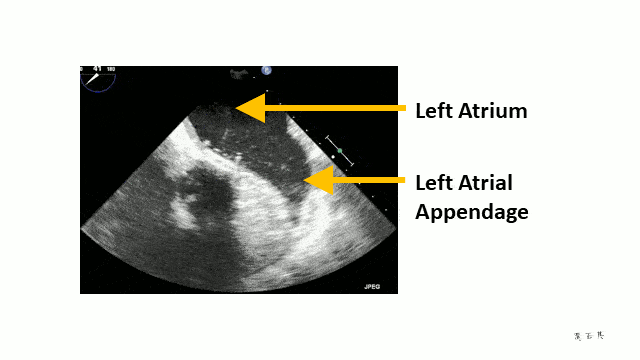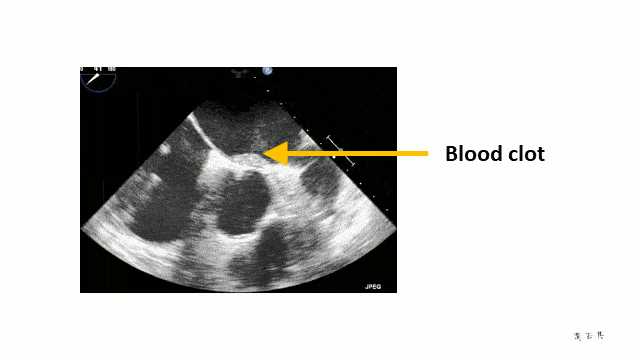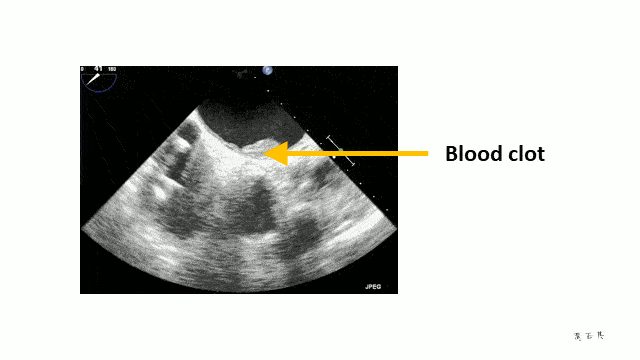
Stroke and Anticoagulation
The turbulent flow can be seen when a transoesophageal echocardiogram is done. It looks like “smoke”.
Unfortunately, clots can form inside the atria because of the turbulent flow and if these break off and reach the brain, they cause a stroke. In fact, they can cut off the blood supply to any organ. For example, the bowels and legs can be affected.
Drugs known as anticoagulants are used to thin the blood and to reduce the risk of clots forming. In the past, warfarin was the only anticoagulant but there are newer drugs known as Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs). These have the advantage of not requiring frequent blood tests, the dose is the same every day and there is less dietary restriction.
Rate and Rhythm Control
The only treatment that reduces the risk of stroke is anticoagulation. The other treatments for atrial fibrillation are for symptom relief.
Drugs such as flecainide and amiodarone and procedures such as DC cardioversion and pulmonary vein isolation are used to return the heart to normal sinus rhythm (rhythm control). Unfortunately, success rates are variable especially in the long term.
Other drugs such as beta blockers, diltiazem and digoxin are used to reduce heart rates.
In summary, atrial fibrillation is the most common arrhythmia. Some risk factors for atrial fibrillation are excessive alcohol and caffeine, high blood pressure, stress and an overactive thyroid. These should be managed if present. The risk for stroke can be estimated by a score known as the CHADSVASC score. Anticoagulation is recommended for those at risk.